Table of Contents
What is cerebral thrombosis?
The brain blood clot also known as thrombosis is a severe blockage of blood from a vessel in the brain. It is usually related to hypertension and cuts of oxygen supply to various parts of the brain. It may result in stroke or death unless treated quickly.
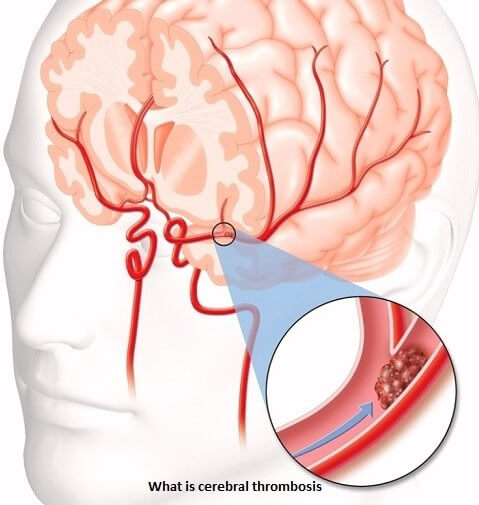
What are the reasons for cerebral thrombosis?
The main reason for cerebral blockage is arterial hypertension, which accounts for 60 to 70% of cases. High blood pressure is responsible for significant structural changes to the walls of cerebral arterioles that can predispose them to plaques. Another reason for cerebral thrombosis is ascribed to the deposition of amyloid substance inside the vessel walls (amyloid angiopathy). Other fundamental causes of cerebral thrombosis are vascular malformations and aneurysms.
What are the symptoms of a cerebral blood clot?
Symptoms usually appear suddenly and can develop very quickly.
The patient can manifest –
- headache
- retching
- nausea
- damage to the state of consciousness and sphincter control
- loss of control over one side of the body
- language problems or aphasia
- sensitivity problems
- coordination problems
The trend can then be aggravated by –
- respiratory irregularities
- instability or increase in blood pressure
- body temperature abnormalities that aggravate a person’s prognosis
Diagnosis
For the diagnosis of cerebral thrombosis, the following diagnostic imaging tests are usually used –
- Cerebral computed tomography (CT), which in urgency can also be done without contrast, allows bleeding and thrombosis to be seen and allows differential diagnosis in relation to a transient ischemic attack.
- MRI of the brain, with gadolinium as a contrast agent, is used to eliminate the presence of underlying malformations, previous bleeding, and micro-bleeding (which can confirm the existence of amyloid angiopathy)
- Angiographic study with CT angiogram finally allows highlighting probable vascular malformations
Surgery for brain thrombosis
Surgery is one of the cornerstones of the treatment of brain thrombosis of any kind, but it is not always practicable, as it depends on the location and on its relationship with the most essential structures of the nervous system. The intervention that requires the opening of the skull is called craniotomy and is performed, for the most part, under general anesthesia, except in selected cases.
The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the clot as possible to establish the exact diagnosis by studying the removed tissue under a microscope, relieving symptoms, improving quality of life and, in some cases, opening a way to other treatments.
The neurosurgeon performs the operation with the aid of very sophisticated microsurgery instruments and always using a surgical microscope and neuro-navigation systems which, through the support of images, guide him to operate precisely and accurately. Thanks to this sophisticated instrumentation, the neurosurgeon can locate brain structures with millimeter precision, both during the preparation phase and during the execution of the intervention.
As for the procedure, the neurosurgeon, after having incised the scalp and having opened a sort of window in the skull, removes the thrombosis through a patient work of progressive isolation and removal of the clot. He then closes the window by repositioning the bone tissue in its place and locking it with metal plates or suture threads.
Modern surgical techniques no longer require total shaving of the hair, but only a strip at the incision. This ensures a definitely more pleasing aesthetic effect and, consequently, increases the patient’s satisfaction.
After the surgery
The period of hospital stay depends on the complexity of the intervention and on the possible post-operative treatment. In the first twelve hours after surgery, the patient will be kept under strict surveillance and monitored in an intensive care unit. It is likely that, in addition to bandaging, a small drainage tube is applied to the wound.
Blood Clot Brain Surgery Cost in India
Essentially the cost of blood clot removal from the brain is the same as doing any other craniotomy procedure, e.g. for tumor. The cost ranges from INR 3.5 lakhs to 6 lakhs or USD 5,000 to 8,500 depending on the hospital and the experience of the doctor. The cost of imaging of various types is about INR 40,000 or USD 560. There may be an extended stay in ICU in some cases as well as a need for physiotherapy if needed. The principal factor for survival is that the blood clot patient needs urgent surgery to remove the threat to his life or permanent damage.